
You need to be relatively close to the router to take advantage of your 5GHz network.Īdditionally, many older devices can’t connect to 5GHz networks. They’re also less likely to experience interference from devices like microwaves and cordless phones.īut their signals simply don’t broadcast as far as 2.4GHz networks – only 230 feet with an 802.11n router.
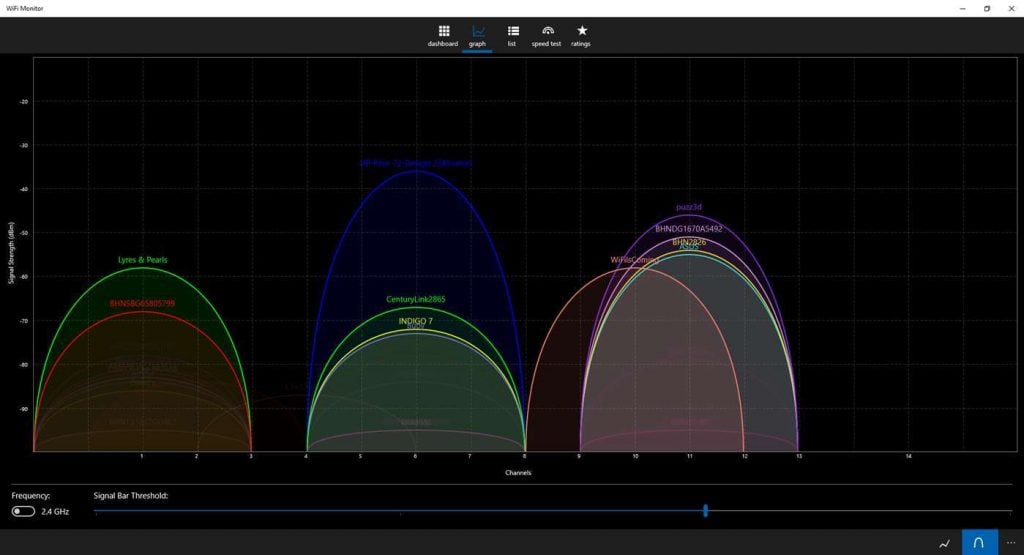
However, 2.4GHz networks are slower than 5GHz networks, so they’re not ideal for bandwidth-intensive tasks like HD streaming.ĥGHz networks can handle much higher speeds, so they’re better-suited for demanding applications. Their signals are far better at penetrating through walls and floors, and they can be detected by all WiFi adapters. On some routers, the 5G network is called only by its name with no “5G” appended to it.Įach frequency band has its own pros and cons.Ģ.4GHz networks have much greater ranges than 5GHz networks – up to 410 feet with an 802.11n router. Routers often broadcast the two versions of your network simultaneously: -5G and -2G. You may recognize these figures from your WiFi connection list. Many modern WiFi routers can broadcast on two different frequency bands: 2.4GHz and 5GHz. These definitions will come in handy later in the process. If You’re in the Market for VPN Service …īefore we begin, let’s cover a few key aspects of your WiFi network.How to Change WiFi Channels on Other Routers.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
